You are here
Innovation & Valorization
The importance of technological innovation for the competitiveness of companies is well established, especially in the current context of globalization, where the companies must confront increasingly strong competition, and satisfy more and more demanding customers. However, the valorization of the results of R&D and inventions is a major concern of universities and R&D centers for their development. From these facts, investment in innovation and valorization must thus be at the heart of the concerns of the companies, universities, research centers, technical centers so that the companies and the university can increase their competitiveness and ensure its survival.
Valorization
The valorization is the set of activities allowing providing added value to the results of the research issued from all domains of research (scientific, technological, social...etc.). The process of valorization, managed by valorization companies, ends with a technological transfer or with the marketing of a finished product.
Value chain
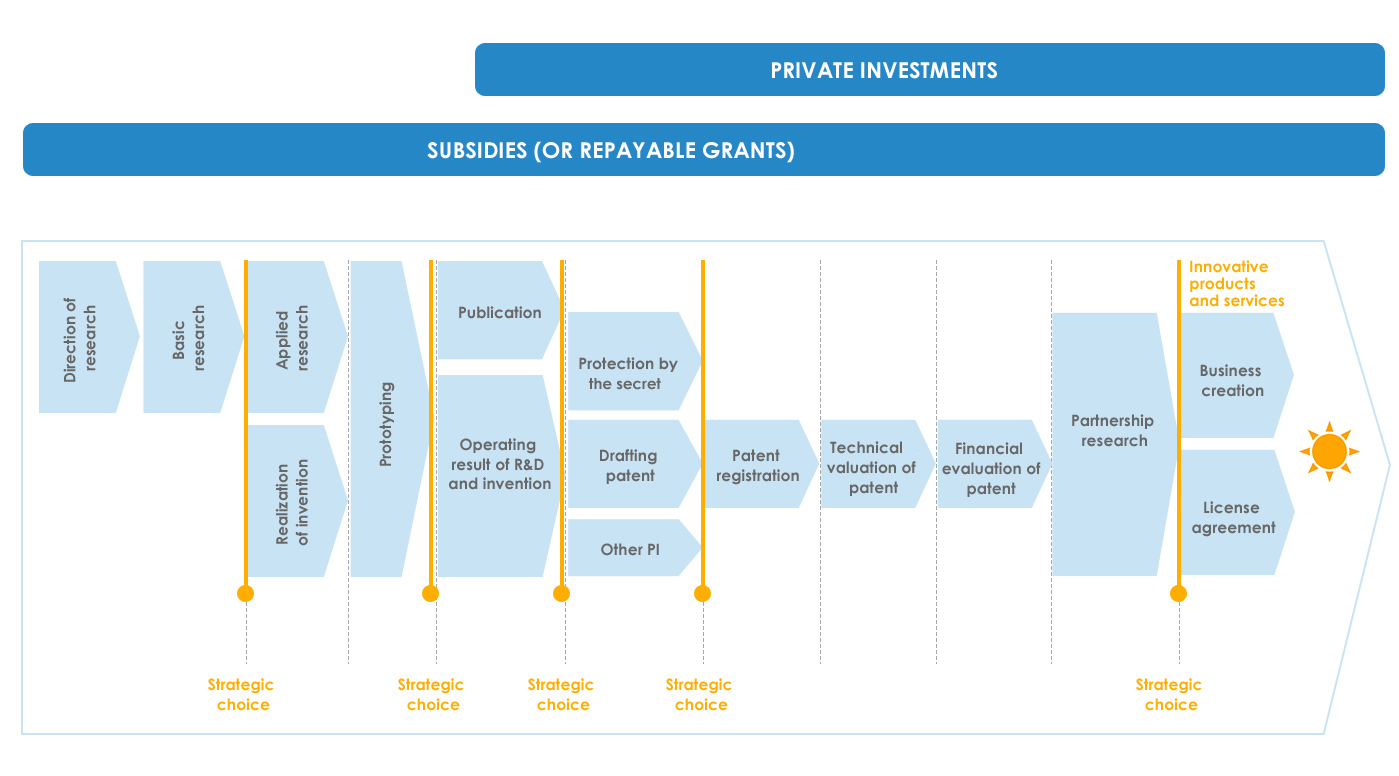
The value chain of the results of R&D is a closed cycle and is presented as follows :
It should be noted that a part of the revenue generated from the marketing of innovative products and services, is used as a source of research funding, upstream of the value chain.
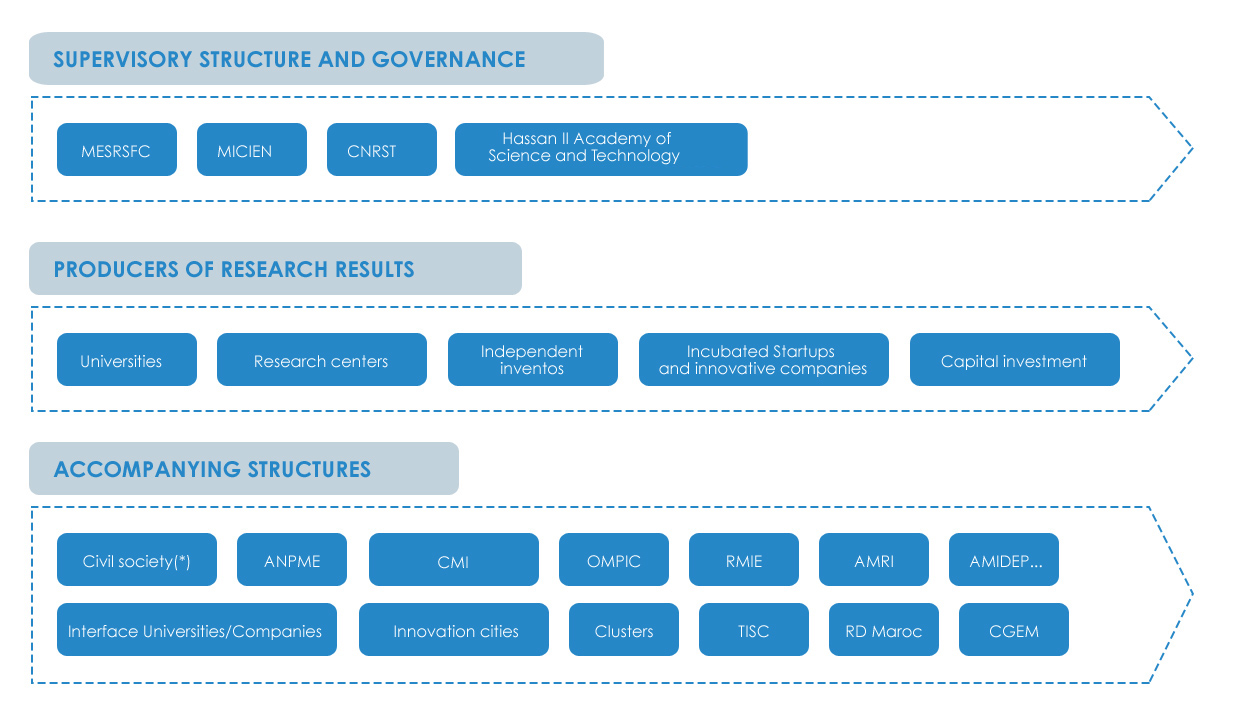
The structures involved in any capacity whether it is in the valorization process are therefore numerous, and include:
- Universities
- The public and private research organizations
- companies OMPIC
- The TISC network (Technology and Innovation Support Centers)
- Banks
- Governments
- Civil society
Below are the organizations involved in the chain of valuation in Morocco according to their respective roles:
Tools of the OMPIC related to the stages of the chain of valuation
The Moroccan Office for Industrial and Commercial Property (OMPIC) has developed operational mechanisms to support project holders in the process of valorization through the optimal use of patents as a tool for information, protection and valuation of inventions and the results of R&D.
The tools developed on the use of patents in the chain of valorizationare illustrated for each stage in the chain of valuation:
Identification of inventions with commercial potential
To achieve this, the OMPIC has developed the Network of Technological Information centers (TISC), which includes active members in the domain of R&D, and that in order to combine and concentrate their efforts around a primary mission which is the technological development of companies and the enhancement of research results of the R&D through judicious use of the system of patents.
The organization of the TISC network relies on focal points hosted at universities and organizations of R&D and representations of companies providing services of search of patent information to detect and repair inventions and results of the R&D for a possible patent protection.
Search services on patents information are:
- Search on the state of the art
- Search of prior art
- Search on patents mapping
- Search on the freedom to operate
Other information related to the TISC are available on the website http://www.tisc.ma
Declaration of the invention to the University for a Preliminary Technical Evaluation.
This activity takes the form of an interview between the inventor and the focal point TISC. The issues discussed, in this interview include:
- Inventors
- Institutions having contributed to the invention
- Potential applications
- Technological value of the invention
- Preliminary Technological Invention
- Agreement revenue sharing
- Distribution of intellectual property
This operation is performed by the focal point TISC at its membership organization.
Protection of the invention through the patent registration
The OMPIC has developed an operational system with research centers to facilitate the procedures for filing and methods of payment of the fees related on filing patent at national and international level. For that purpose, partnership agreements and promotion of research by filing patent are signed with public and private universities and also with organizations of research aiming to deploy this system. The patent registration is ensured by the focal point TISC at its parent organization, in coordination with the researcher and/or inventor.
To encourage universities and SMEs to use the patents system, a reduction in tariffs
is granted to universities, SMEs and inventors to encourage them to use the patents system.
Marketing of the invention
After the registration of the patent application, the team responsible for the valorization must analyze the market of the invention through:
- Research on internet
- Analysis and estimation of market sizes
- Analysis of competition
- Freedom of use of IP.
Research of mapping patents, provided for members of the TISC network, allows to have elements on the market of the invention, and this through the research and analysis of patents published in the theme of the invention. This search is transmitted by the focal point TISC and prepared by the OMPIC.
valorization strategy
The decision to pursue the valuation depends essentially on the result of the preliminary technical assessment and market analysis. If the valuation team decides not to select the invention, a notification is sent to the researcher and / or the inventor. If the invention is selected, the valuation process continues with the choice of a development strategy:
- Technical and/or economic maturation of the project
- Patent licensing
- Creating enterprises (start-up or Spin-off)
The choice of one of these strategies depends on the valorization policy of the organization of research.
The first strategy is to add value through technical, legal and economic maturation of the project through:
- Development of prototype
- Protection of intellectual property at the international level
- Creation of a business plan
The licensing is a commercial exploitation of intellectual property including patents. At this stage, several questions are treated in connection with negotiation and licensing agreements:
The principal terms of the license agreement:
- Exclusivity, application, territory
- Duration of license
- Right against sub-licensors
- Royalties and lump sum
- License management and check mechanism
The creation of start up for the exploitation of the results of R&D and inventions is a relapsing within the research organizations. This operation consists of creating an start up by the research organization for the development and commercialization of products objects of enhancement.
Tools for innovation financing
Any result of R&D or invention aims to achieve its marketing. This outcome cannot exist without the creation of the companies on the basis of the promising idea of product development and for the successful commercialization of the result in a competitive market. For this purpose, the financial means available are crucial in deciding the action to be a result of R&D or invention.
In Morocco, financing tools of innovative projects can take different forms:
- Public aids developed with the strategy Morocco innovation and which are subsidies(RMIE, support for scientific projects, Technological Services Network, Imitiaz and Innov'Act) and repayable subsidies at 0% (Intilak and Tatwir). More information on the Moroccan center for innovation which manages financing tools INTILAK? TATWIR and PTR on the website http://www.cmi.net.ma.
- Philanthropy with civil society (call for project, selection, advice and support, fundraising...).
- Private investment in innovative project equity of the project holder or seeking outside investors.
The crossing of natures of financement with the chain of optimization of the results of R&D and invention shows the predominance of subsidies on private investments (equity of the project leader and external investments).